|
How does the flow of energy across ecosystem boundaries impact food web structure?
|
Classic food webs depict primary producers fueling secondary production via "green” plant-based food webs, but increasing evidence suggests many animals also derive energy from “brown” detrital food webs (Pauli et al. 2019). Up to 90% of all primary production escapes herbivory and is decomposed in brown webs where bacteria and fungi transform recalcitrant material like cellulose into usable biomolecules like amino acids (Fig. 1). This process recycles nutrients and increases resource availability, but the impact of this brown energy on secondary consumers and trophic structure remains uncertain.
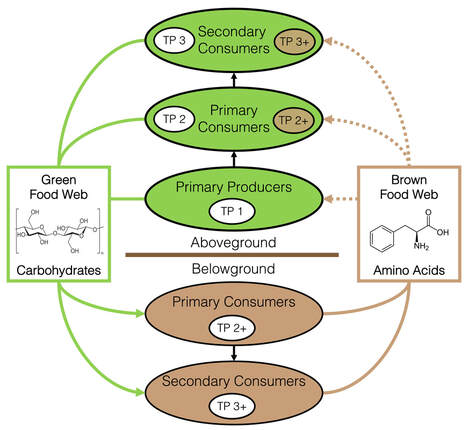 Fig 1. Conceptual diagram illustrating the linking of "green" and "brown" energy channels in food webs. Microbial detritivores transform recalcitrant carbohydrates into useable biomolecules like amino acids that are used by higher order consumers, with consequences for food web structure. Fig 1. Conceptual diagram illustrating the linking of "green" and "brown" energy channels in food webs. Microbial detritivores transform recalcitrant carbohydrates into useable biomolecules like amino acids that are used by higher order consumers, with consequences for food web structure.
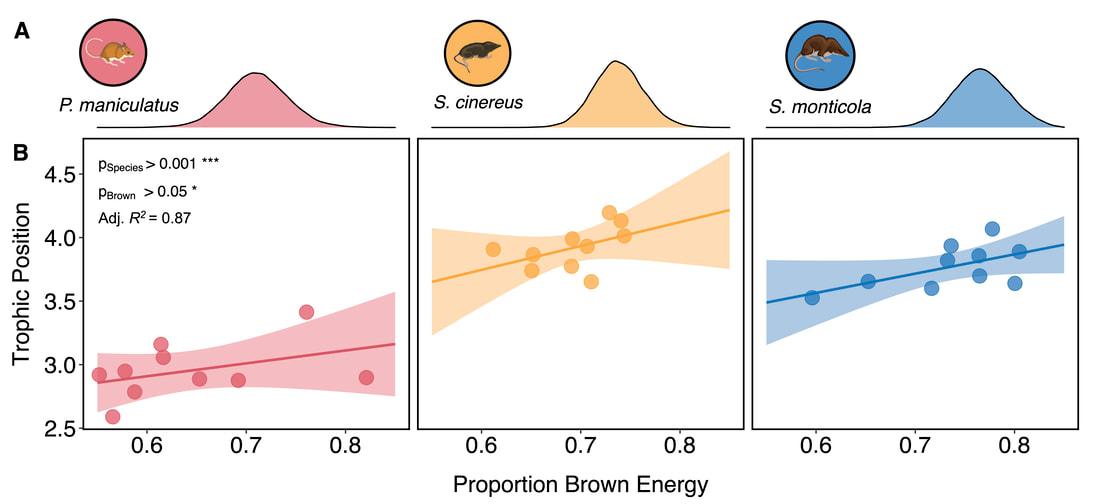
I use state-of-the-art carbon (δ13C) and nitrogen (δ15N) isotope analysis of individual amino acids to trace the flow of green and brown energy through terrestrial food webs to map energy flow and quantify food web linkages. Because animals cannot synthesize essential amino acids (AAess), they must acquire these molecules through their diet or via gut microbes. Importantly, green and brown energy sources exhibit distinct δ13C ratios among AAess due to unique biosynthetic pathways (i.e., isotopic "fingerprints") that can then be used quantify food web coupling (Manlick and Newsome 2022) . For example, using biological collections from the University of New Mexico Museum of Southwestern Biology (UNM-MSB), I sampled small mammal consumers in New Mexico's sky islands to assess the impact of brown energy on food web structure and found that small mammals couple energy channels which in turn drives food web structure (Fig. 2).
|
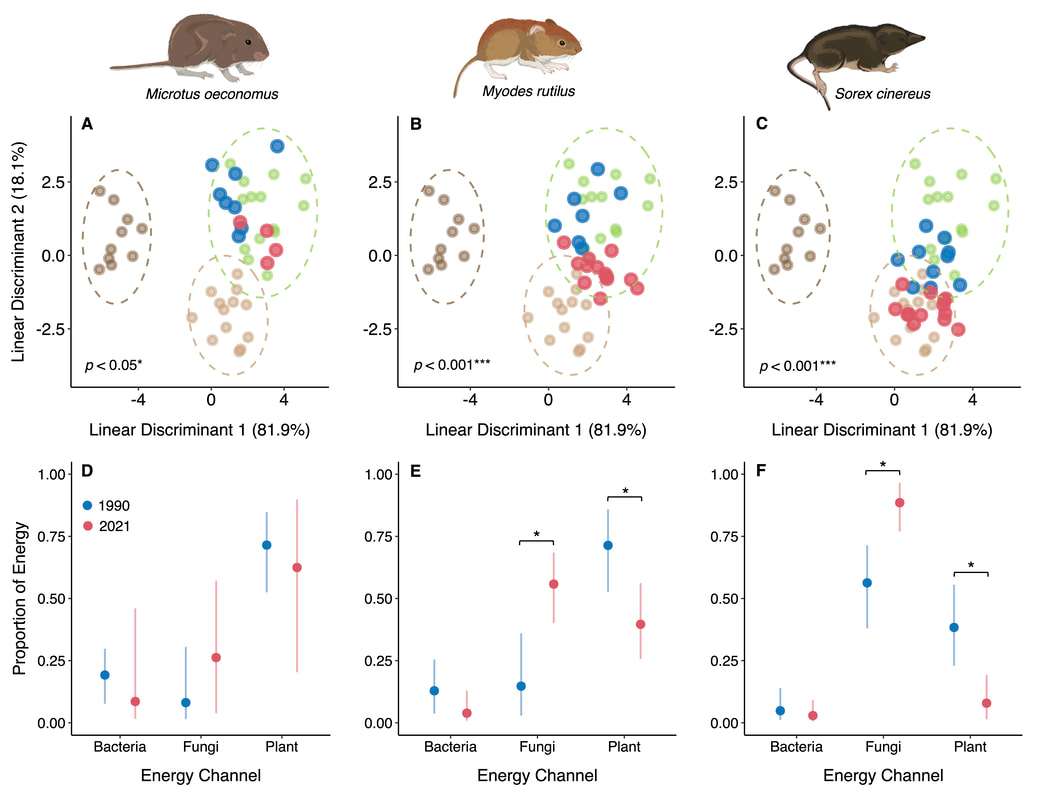
Ongoing Research: I am now using similar approaches in Arctic and Subarctic Alaska to trace food web linkages in response to climate-mediated permafrost decay. We predicted that increased microbial decomposition following permafrost degradation would lead to increased use of "brown" food webs by higher order consumers, and we observed significant shifts across species and functional groups (Fig. 3).
This material is based upon work supported by the NSF Postdoctoral Research Fellowships in Biology Program under Grant No. 2010712. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Support for this work is provided by:
Support for this work is provided by: